As nursing students, understanding the motivation and behavior of our patients is crucial to providing effective and compassionate care. One theory that can aid us in this pursuit is Maslow’s Theory of Needs. Developed by psychologist Abraham Maslow, this theory is based on the idea that humans have a hierarchy of needs that must be met in order to achieve self-actualization, or the realization of our full potential as individuals. In this article, we will explore Maslow’s Theory of Needs and how it applies to nursing practice.
Overview of Maslow’s Theory of Needs
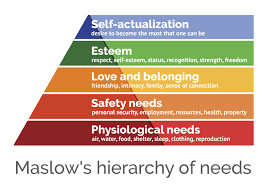
At the core of Maslow’s theory is the belief that humans have a set of needs that must be satisfied in a specific order. These needs are arranged in a hierarchy, with the most basic and essential needs at the bottom of the pyramid and the more complex and abstract needs at the top. The hierarchy of needs is as follows:
- Physiological needs – These are the most basic needs, such as food, water, air, and shelter. They must be met before any other needs can be addressed.
- Safety needs – Once physiological needs are met, humans require a sense of safety and security, both physically and emotionally.
- Love and belonging needs – After safety needs are met, humans require social interaction and a sense of belonging.
- Esteem needs – Once love and belonging needs are met, humans require respect and recognition from others and a sense of self-esteem.
- Self-actualization needs – Finally, once all other needs are met, humans seek to achieve their full potential and become the best versions of themselves.
The hierarchy of needs explains how human motivation and behavior is driven by our needs. It suggests that as each need is met, individuals move up the hierarchy and become motivated by the next level of needs.
Physiological Needs
The first level of Maslow’s hierarchy is physiological needs. These are the most basic and fundamental needs that must be met before any other needs can be addressed. Examples of physiological needs include food, water, air, shelter, sleep, and warmth. As nursing students, it is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of physiological needs in our patients. Patients who are hungry, thirsty, or cold may feel irritable or anxious. They may also experience physical symptoms such as headaches, nausea, or dizziness.
To address physiological needs, nursing students should ensure that their patients are well-fed, hydrated, and comfortable. This may involve providing meals, drinks, or blankets, and adjusting the temperature in the patient’s room. By addressing these basic needs, nursing students can help their patients feel more comfortable and at ease.
Safety Needs
Once physiological needs are met, individuals require a sense of safety and security. This includes physical safety as well as emotional safety. Examples of safety needs include protection from physical harm, financial security, and emotional stability. Patients who are anxious, fearful, or experiencing trauma may have unmet safety needs.
As nursing students, it is important to provide a safe and secure environment for our patients. This may involve ensuring that the patient’s room is free from hazards, providing emotional support and reassurance, and advocating for the patient’s needs and concerns. By addressing safety needs, nursing students can help their patients feel secure and protected.
Love and Belonging Needs
Once safety needs are met, humans require social interaction and a sense of belonging. This includes the need for love, friendship, and community. Examples of love and belonging needs include spending time with family and friends, feeling connected to a community, and feeling loved and appreciated.
As nursing students, it is important to provide emotional support and create a sense of community for our patients. This may involve listening to the patient’s concerns and providing reassurance, facilitating social interaction between the patient and their loved ones, and encouraging participation in group activities. By addressing love and belonging needs, nursing students can help their patients feel connected and valued.
Esteem Needs
After love and belonging needs are met, individuals require respect and recognition from others as well as a sense of self-esteem. This includes the need for achievement, mastery, and status. Examples of esteem needs include feeling respected and appreciated by others, receiving recognition for accomplishments, and feeling self-confident and capable.
As nursing students, it is important to encourage and support our patients’ self-esteem and sense of achievement. This may involve acknowledging their accomplishments and strengths, providing opportunities for skill-building and self-expression, and advocating for their needs and rights. By addressing esteem needs, nursing students can help their patients feel valued and capable.
Self-Actualization Needs
The final level of Maslow’s hierarchy is self-actualization needs. This involves achieving one’s full potential and becoming the best version of oneself. Examples of self-actualization needs include creativity, self-expression, personal growth, and a sense of purpose and meaning.
As nursing students, it is important to support and encourage our patients’ pursuit of self-actualization. This may involve providing opportunities for creative expression and personal growth, encouraging the pursuit of hobbies and interests, and supporting the patient’s sense of purpose and meaning. By addressing self-actualization needs, nursing students can help their patients achieve their full potential and become the best versions of themselves.
Application of Maslow’s Theory in Nursing
As nursing students, we can apply Maslow’s Theory of Needs in our practice by assessing our patients’ needs and developing care plans that address their specific needs. By identifying where our patients fall on the hierarchy of needs, we can determine which needs are most urgent and develop interventions that are tailored to their specific needs.
For example, if a patient is experiencing physical discomfort, addressing their physiological needs may be the top priority. This may involve providing pain medication, ensuring the patient is well-fed and hydrated, and ensuring their physical comfort. If a patient is feeling isolated and disconnected, addressing their love and belonging needs may be a priority. This may involve facilitating social interaction with their loved ones, providing opportunities for group activities, and listening to the patient’s concerns and needs.
Critiques of Maslow’s Theory of Needs
While Maslow’s Theory of Needs has been widely accepted and applied in various fields, including nursing, it has also been subject to criticism and limitations. Some critics argue that the hierarchy of needs is too simplistic and fails to account for individual differences and cultural variations. Others argue that the theory is too focused on individual needs and neglects the importance of collective and societal needs.
As nursing students, it is important to use critical thinking and evaluate the limitations and critiques of the theory. This may involve acknowledging individual differences and cultural variations in needs, and developing care plans that are tailored to the specific needs of our patients. It may also involve advocating for the importance of collective and societal needs in nursing practice and addressing the social determinants of health that may affect our patients’ well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Maslow’s Theory of Needs is a valuable framework for understanding human motivation and behavior, and applying this understanding to nursing practice. By addressing our patients’ specific needs and tailoring our care plans to meet these needs, we can provide compassionate and effective care that addresses the whole person. While the theory is not without its critiques and limitations, nursing students can use critical thinking and creativity to address these challenges and provide care that is sensitive to the diverse needs of our patients.
FAQs
Q: How do you apply Maslow’s hierarchy of needs to patient care?
A: Applying Maslow’s hierarchy of needs to patient care involves identifying the patient’s needs at each level of the hierarchy and addressing those needs in order. For example, if a patient is hungry and thirsty, the nurse would address their physiological needs by providing food and water before moving on to address other needs such as safety, belongingness, esteem, and self-actualization.
Q: What is safety Maslow’s hierarchy of needs nursing?
A: Safety is the second level of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, and it pertains to the need for security, stability, and freedom from harm. In the context of nursing, safety needs can manifest in various ways, such as the need for a safe and clean environment, protection from injury, and access to medical care and resources.
Q: Which concepts does the nursing student understand are tiers in Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
A: Nursing students are typically taught that Maslow’s hierarchy of needs consists of five tiers or levels, starting with physiological needs at the base of the hierarchy, followed by safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization.
Q: What is self-actualization in nursing?
A: Self-actualization is the highest level of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, and it pertains to the realization of one’s full potential and the attainment of personal fulfillment. In the context of nursing, self-actualization can manifest in various ways, such as the patient’s ability to engage in meaningful activities, pursue their interests, and maintain a sense of purpose and meaning.
Q: What is the hierarchy of nursing process?
A: The hierarchy of the nursing process is a framework for nursing practice that consists of five stages: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. This process is used to identify and address the patient’s health care needs in a systematic and holistic manner.
Q: What are the 5 priorities of nursing care?
A: The 5 priorities of nursing care are commonly referred to as the “Five Rights” of nursing, and they include the right patient, right medication, right dose, right route, and right time. These priorities are designed to ensure patient safety and the effective delivery of care.
Q: What are the 5 stages of nursing process?
A: The 5 stages of the nursing process are assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. Each stage is designed to identify and address the patient’s health care needs in a systematic and holistic manner.
Q: What are the ABC of nursing assessment?
A: The ABC of nursing assessment stands for airway, breathing, and circulation. This is a critical first step in the nursing assessment process, as it helps to identify any potential life-threatening issues that need to be addressed immediately.
Q: What is the importance of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs in health?
A: Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is important in health care because it provides a framework for understanding the various needs and motivations of patients. By identifying and addressing these needs in a systematic and holistic manner, health care professionals can provide more effective and patient-centered care.
Q: How can Maslow’s theory be used to assist human service professionals in providing care?
A: Maslow’s theory can be used by human service professionals to better understand their clients’ needs and motivations. By identifying and addressing these needs in a systematic and holistic manner, human service professionals can provide more effective and client-centered care. This can include addressing basic needs such as food and shelter, as well as higher-level needs such as self-esteem and self-actualization.
A Page will cost you $12, however, this varies with your deadline.
We have a team of expert nursing writers ready to help with your nursing assignments. They will save you time, and improve your grades.
Whatever your goals are, expect plagiarism-free works, on-time delivery, and 24/7 support from us.
Here is your 15% off to get started.
Simply:
- Place your order (Place Order)
- Click on Enter Promo Code after adding your instructions
- Insert your code – Get20
All the Best,
Cathy, CS