Nursing Informatics Essay
Nursing informatics is a specialty that integrates nursing science with multiple information and analytical sciences to identify, define, manage, and communicate data, information, knowledge, and wisdom in nursing practice.
It facilitates the integration of data, information, and knowledge to support nurses, patients, and other healthcare providers in their decision-making in all roles and settings. This support is achieved through the use of information structures, information processes, and information technology.
The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive guide on how to write a nursing informatics essay. Whether you are a novice writer or an experienced researcher, this guide will offer valuable insights and practical tips to help you create a well-structured and impactful paper.
Structure of a Nursing Informatics Essay
Abstract
The abstract is a concise summary of the paper, typically 150-250 words, highlighting the purpose, methods, key findings, and implications of the study. It provides a quick overview for readers to determine the relevance of the paper to their interests.
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the paper by providing background information, stating the problem or research question, and outlining the paper’s objectives. It should capture the reader’s interest and clearly define the scope and significance of the study.
Literature Review
The literature review synthesizes existing research related to the paper’s topic. It identifies key studies, highlights gaps in the current knowledge, and establishes the context for the research. A well-organized literature review demonstrates the author’s understanding of the field and justifies the need for the study.
Methodology
The methodology section details the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques used in the study. It should be thorough and transparent, allowing other researchers to replicate the study if needed. This section also discusses any ethical considerations and limitations of the study.
Results
The results section presents the findings of the study, including data analysis and interpretation. It should be clear and concise, using tables, figures, and charts to illustrate key points. The results should be presented objectively, without interpretation or bias.
Discussion
The discussion section interprets the results in the context of existing literature. It explores the implications of the findings, addresses any limitations, and suggests areas for future research. This section connects the study’s results to the broader field of nursing informatics.
Conclusion
The conclusion summarizes the key points of the paper, emphasizing the contributions to the field and potential impacts on practice. It should reinforce the importance of the study and provide a clear take-home message for readers.
References
The references section lists all the sources cited in the paper, formatted according to the appropriate style guide (e.g., APA, MLA). Accurate and thorough referencing is crucial for academic integrity and allows readers to locate the sources.
Writing the Nursing Informatics Paper

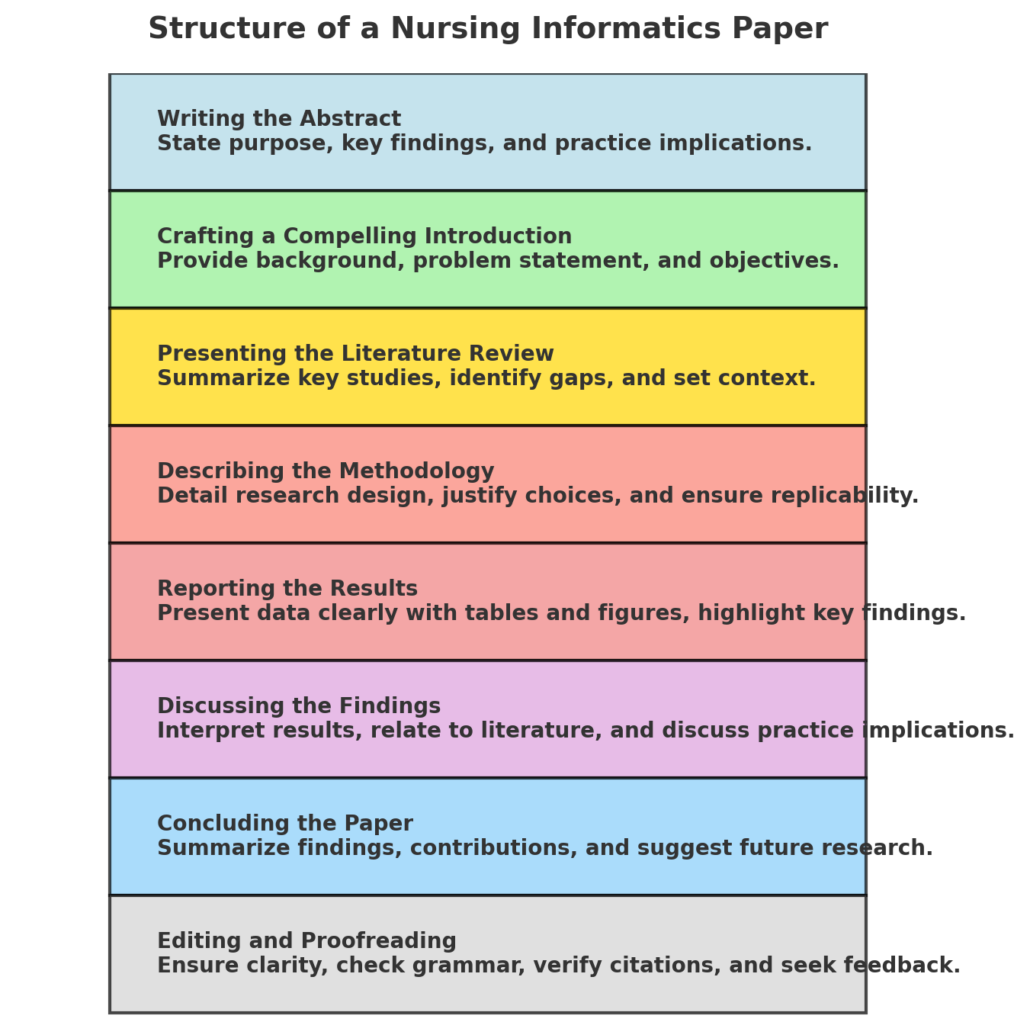
Writing the Abstract
- Purpose and Scope: Begin your abstract by stating the purpose and scope of your study. Clearly articulate the research question or problem addressed.
- Key Findings: Summarize the key findings of your study, highlighting the most important results and their implications on the nursing profession.
- Implications for Practice: Conclude the abstract with a brief discussion of the implications of your findings for nursing practice and future research.
Crafting a Compelling Introduction
- Background Information: Provide background information on the topic, including relevant statistics and previous research findings. This sets the stage for your study and highlights its significance.
- Problem Statement: Clearly state the problem or research question that your study addresses. Explain why this issue is important in the nursing field and worthy of investigation.
- Objectives and Research Questions: Outline the specific objectives and research questions of your study. These should align with the problem statement and guide the direction of your research.
Presenting the Literature Review
- Summarizing Key Studies: Summarize the key studies related to your topic, highlighting their findings and methodologies. This provides a foundation for your research and demonstrates your understanding of the field.
- Identifying Gaps in the Literature: Identify any gaps or inconsistencies in the existing literature. This justifies the need for your study and indicates how it will contribute to the field.
- Establishing the Context for Your Research: Establish the context for your research by connecting your study to the broader field of nursing informatics. Explain how your research will address the identified gaps and contribute new knowledge.
Describing the Methodology
- Detailing Research Design and Methods: Describe the research design and methods used in your study. Be specific about the techniques and procedures employed.
- Justifying Methodological Choices: Justify your methodological choices by explaining why they are appropriate for your research question. Discuss any limitations and how you addressed them.
- Ensuring Replicability: Ensure that your methodology is detailed enough to allow other researchers to replicate your study. This enhances the reliability and validity of your findings.
Reporting the Results
- Presenting Data Clearly: Present your data clearly and concisely. Use descriptive text, tables, and figures to illustrate your findings.
- Using Tables and Figures: Tables and figures should be used to present data in an easily understandable format. Ensure they are labeled correctly and referenced in the text.
- Highlighting Key Findings: Highlight the most important findings of your study. Focus on the results that directly address your research questions or hypotheses.
Discussing the Findings
- Interpreting Results: Interpret your results in the context of the existing literature. Discuss how your findings support or contradict previous studies.
- Relating Findings to Existing Literature: Relate your findings to the broader field of nursing informatics. Discuss their implications for theory, practice, and future research.
- Discussing Implications for Nursing Practice: Discuss the practical implications of your findings for nursing practice. Consider how your research can inform clinical practice, policy, and education.
Concluding the Paper
- Summarizing Key Points: Summarize the key points of your paper, emphasizing the most important findings and their implications.
- Highlighting Contributions to the Field: Highlight the contributions of your study to the field of nursing informatics. Discuss how your research advances knowledge and practice.
- Suggesting Areas for Future Research: Suggest areas for future research based on your findings. Identify any unanswered questions or new directions for investigation.
Editing and Proofreading
- Ensuring Clarity and Coherence: Ensure that your paper is clear and coherent. Each section should logically flow into the next, and your arguments should be easy to follow.
- Checking for Grammatical and Typographical Error: Check your paper for grammatical and typographical errors. Use tools like spell check and grammar check, and consider having someone else review your work.
- Verifying Proper Citation and Referencing: Verify that all sources are properly cited and referenced according to the required style guide. This ensures academic integrity and allows readers to locate your sources.
- Seeking Feedback from Peers and Mentors: Seek feedback from peers and mentors to improve your paper. They can provide valuable insights and help identify any weaknesses or areas for improvement.
Types of Nursing Informatics Papers
Research Papers
Research papers in nursing informatics involve the systematic investigation of various aspects of informatics in nursing. These papers present original research, including the study’s background, methods, results, and conclusions. They contribute new knowledge to the field and are typically structured with an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Review Papers
Review papers provide a comprehensive summary of existing research on a particular topic within nursing informatics. They analyze, evaluate, and synthesize previous studies to identify trends, gaps, and future research directions. These papers do not present new research but rather compile and critically assess existing knowledge.
Case Studies
Case studies in nursing informatics focus on detailed examination and analysis of specific instances within real-world settings. They explore the implementation, challenges, and outcomes of informatics solutions in clinical practice. Case studies are valuable for understanding practical applications and implications of nursing informatics.
Choosing a Topic for Your Essay on Nursing Informatics
Relevance to Current Trends and Issues
When choosing a topic for your nursing informatics paper, consider its relevance to current trends and issues in healthcare. Topics that address emerging technologies and information systems, policy changes, or innovative practices are likely to attract interest and contribute valuable insights to the field.
Significance to Nursing Practice and Patient Care
Select a topic that has significant implications for nursing practice and patient care. The best topics are those that can lead to improvements in clinical practice, patient outcomes, or healthcare delivery. Consider how your research can address practical challenges faced by nurses and healthcare providers by improving clinical decision-making and reducing medical errors.
Examples of Potential Topics
- Implementation of Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Explore the challenges and benefits of implementing EHRs in healthcare settings. Discuss how EHRs impact workflow, data accuracy, and patient care, and analyze strategies for successful implementation.
- Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring
Examine the role of telehealth and remote patient monitoring in modern healthcare. Investigate how these technologies enhance access to care, clinical research, improve patient outcomes, and address barriers such as geographical distance and resource limitations.
- Data Analytics in Nursing
Analyze the use of data analytics to improve clinical decision-making and patient care. Discuss how data analytics can identify patterns, predict outcomes, and inform evidence-based practice.
- Impact of Informatics on Patient Outcomes
Investigate the direct and indirect impacts of nursing informatics on patient outcomes. Consider factors such as error reduction, patient satisfaction, and overall quality of care.
Conducting a Literature Review
Identifying Relevant Sources
Begin your literature review by identifying relevant sources. Use databases such as PubMed, CINAHL, and Google Scholar to find peer-reviewed articles, books, and reports. Keywords related to your topic will help you locate pertinent literature.
Evaluating the Quality of Sources
Evaluate the quality of your sources by considering their credibility, relevance, and publication date. Peer-reviewed journal articles and reputable books are generally reliable, whereas outdated or non-peer-reviewed sources may not provide accurate information.
Synthesizing Information from Multiple Sources
Synthesize information from multiple sources by comparing and contrasting their findings. Identify common themes, conflicting results, and gaps in the literature. This synthesis will form the basis of your literature review.
Organizing the Literature Review
Thematic Approach
Organize your literature review thematically by grouping studies with similar themes or findings. This approach helps highlight key areas of agreement and disagreement within the literature.
Chronological Approach
A chronological approach organizes studies based on their publication date. This method is useful for demonstrating how research on your topic has evolved over time.
Methodological Approach
The methodological approach groups studies based on their research methods. This is particularly useful for comparing different research designs and their outcomes.
Developing a Strong Methodology
Research Design for the Nursing Informatics Paper
Qualitative Methods
Qualitative methods involve collecting non-numerical data to understand concepts, experiences, or phenomena. Common techniques include interviews, focus groups, and content analysis. These methods are useful for exploring complex issues in depth.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods involve collecting numerical data to identify patterns, test hypotheses, and make predictions. Techniques include surveys, experiments, and statistical analysis. These methods are ideal for studying large populations and establishing generalizable findings.
Mixed Methods
Mixed methods combine qualitative and quantitative approaches to provide a comprehensive understanding of the research problem. This approach allows for the triangulation of data, enhancing the validity and reliability of the findings.
Data Collection Techniques
Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are efficient tools for collecting data from large groups. They can include closed-ended questions for quantitative analysis or open-ended questions for qualitative insights.
Interviews
Interviews involve direct, one-on-one interactions to gather detailed information. They can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured, depending on the research goals.
Observational Studies
Observational studies involve systematically recording behaviors or events in their natural settings. This method is useful for studying real-world interactions and practices.
Data Analysis Methods
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis involves using mathematical techniques to analyze quantitative data. Common methods include descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and regression analysis.
Content Analysis
Content analysis involves systematically coding and interpreting qualitative data. This method is useful for identifying patterns and themes within textual health information.
Ethical Considerations in Nursing Informatics Research
Ethical considerations are paramount in nursing informatics research. Ensure informed consent, protect participants’ confidentiality, and obtain necessary approvals from institutional review boards (IRBs). Address any potential conflicts of interest and maintain transparency throughout the research process.
Formatting and Submission Guidelines
Adhering to Journal or Institution Guidelines
Adhere to the submission guidelines provided by the journal or institution. These guidelines often include specific formatting, length, and style requirements.
Using Appropriate Formatting Styles (e.g., APA, MLA)
Use the appropriate formatting style for your paper, such as APA or MLA. Follow the guidelines for headings, citations, references, and overall document layout.
Preparing Supplemental Materials
Prepare any supplemental materials required for your submission, such as appendices, datasets, or multimedia content. Ensure these materials are well-organized and properly referenced.
Submitting the Paper
Submit your paper according to the journal or institution’s submission process. This may involve online submission, email, or physical delivery. Ensure you meet any deadlines and include all required documents.
Conclusion
Engaging in nursing informatics research is essential for advancing the field and improving healthcare outcomes. Your contributions can lead to significant improvements in clinical practice, patient care, and healthcare delivery in the area of nursing.
If you need assistance with your nursing informatics paper, consider seeking help from our academic writing services. Our team of professional writers will provide expert guidance and support, ensuring your paper is well-written and impactful.
Nursing Informatics Paper FAQs
- What is the definition of nursing informatics? Nursing informatics is a specialty that integrates nursing science with multiple information and analytical sciences to identify, define, manage, and communicate data, information, knowledge, and wisdom in nursing practice.
- What are the key components of a nursing informatics paper? The key components of a nursing informatics paper include an abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and references.
- How can nursing informatics improve patient care? Nursing informatics is a field that can improve patient care by enhancing the management of electronic health records, enabling telehealth services, and supporting data analytics, which can help reduce errors, streamline workflows, and ensure better health outcomes.
- What are some examples of potential topics for a nursing informatics paper? Potential topics for an essay on nursing informatics include the implementation of electronic health records, the role of telehealth and remote patient monitoring, the use of data analytics in nursing, and the impact of informatics on patient outcomes.