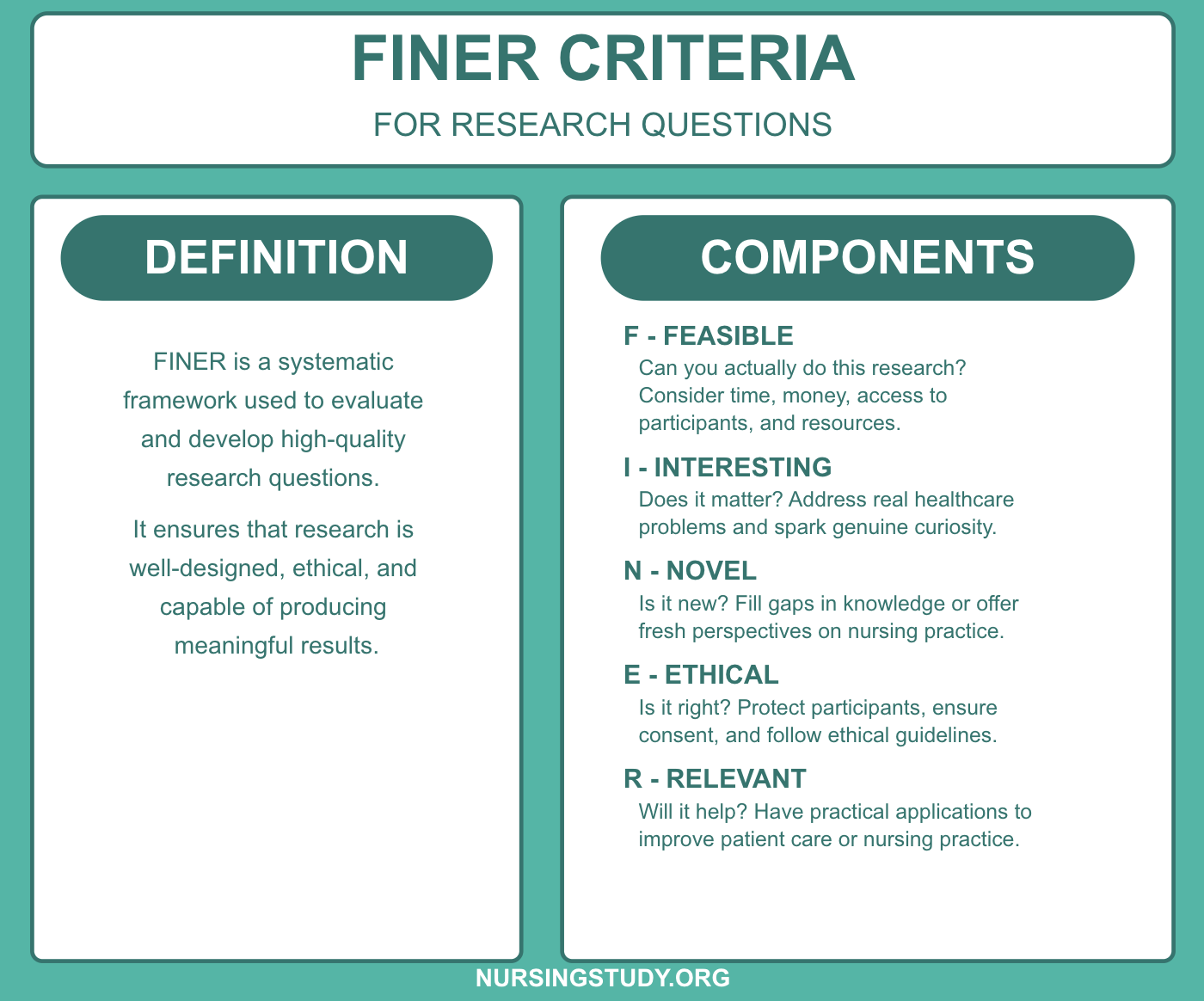
FINER Criteria: FINER is a systematic framework used to evaluate and develop high-quality research questions. It ensures that research is well-designed, ethical, and capable of producing meaningful results.
F – Feasible Can you actually do this research? Consider your time, money, access to participants, and available resources.
I – Interesting Does it matter? The question should address real healthcare problems and spark genuine curiosity in the nursing field.
N – Novel Is it new? Your research should fill a gap in existing knowledge or offer a fresh perspective on nursing practice.
E – Ethical Is it right? Protect participants, ensure consent, maintain confidentiality, and follow ethical guidelines.
R – Relevant Will it help? The research should have practical applications that can improve patient care or nursing practice
The FINER framework provides a systematic method for evaluating and developing high-quality research questions in nursing research. Each component serves as a critical checkpoint for ensuring the robustness of your research inquiry.
FINER Criteria components
Feasible
Research feasibility is the cornerstone of a successful research project. When assessing feasibility, nursing students must consider multiple dimensions:
Key Feasibility Considerations:
- Resource Availability
- Financial resources
- Time constraints
- Access to research participants
- Technological and institutional support
- Practical Limitations
- Geographic restrictions
- Sample population accessibility
- Potential recruitment challenges
- Ethical approval processes
Example of a Feasible Research Question: “What are the perceived barriers to pain management among nurse-led interventions for older adults in rural community settings?”
Interesting
An compelling research question should spark intellectual curiosity and address meaningful gaps in nursing knowledge.
Characteristics of an Interesting Research Question:
- Addresses current healthcare challenges
- Explores innovative nursing practice approaches
- Potential for significant healthcare providers insights
- Demonstrates novel perspective on existing problems
Example: “How do mindfulness-based interventions impact mental health nursing outcomes for patients with advanced cancer?”
Novel
Novelty requires pushing the boundaries of existing nursing research topics and offering unique perspectives.
Novelty Assessment Criteria:
- Identifies unexplored research areas
- Challenges existing healthcare paradigms
- Offers innovative methodological approaches
- Addresses emerging healthcare policies
Example: “What is the effectiveness of technology-enhanced nursing care in improving patient care outcomes for chronic disease management?”
Ethical
Ethical considerations are paramount in nursing research.
Ethical Research Question Development:
- Prioritizes participant welfare
- Ensures informed consent
- Maintains confidentiality
- Minimizes potential harm
- Adheres to institutional review board guidelines
Example: “How can nursing interventions support dignified end-of-life care while respecting patient autonomy?”
Relevant
Relevance ensures the research contributes meaningfully to nursing practice and broader healthcare understanding.
Relevance Evaluation:
- Addresses current healthcare challenges
- Potential for practical implementation
- Aligns with evidence-based practice
- Offers actionable insights for healthcare providers
Example: “What strategies can improve clinical nursing communication effectiveness in pediatric nursing settings?”
Research Question Comparison: Without vs With FINER Criteria

Key Observations from the Comparison:
1. Specificity is Critical The vague question “Does stress affect nurses?” lacks any specificity, making it impossible to design a meaningful study. The FINER version identifies exact variables: 12-week duration, mindfulness-based intervention, burnout and job satisfaction as outcomes, critical care nurses as the population, and urban teaching hospitals as the setting.
2. From Unmeasurable to Measurable The poor question doesn’t specify what to measure or how. The FINER question clearly identifies measurable outcomes (burnout levels, job satisfaction scores) that can be quantified and analyzed using validated instruments.
3. Scope Management Without FINER criteria, research questions become too broad to be practically achievable. The FINER approach narrows the scope to a manageable study while maintaining significance and impact.
4. Research Design Clarity The vague question leaves researchers guessing about methodology, while the FINER question implicitly suggests an intervention study design with pre/post measurements in a specific population.
5. Practical Implementation The FINER question can be immediately translated into a research protocol with clear inclusion criteria, intervention protocols, and outcome measures. The poor question would require complete redesign before any research could begin.
6. Stakeholder Value The FINER question clearly communicates value to multiple stakeholders: hospital administrators see retention solutions, nurses see burnout reduction strategies, and patients benefit from improved care quality. The vague question offers no clear value proposition.
7. Literature Review Focus The FINER question provides clear search terms for literature review (mindfulness interventions, critical care nursing, burnout measurement), while the poor question is too broad to conduct targeted literature searches.
Bottom Line: Using FINER criteria transforms an unusable research question into a well-defined, achievable study that can produce actionable insights for nursing practice.
15 examples of FINER Criteria Research Questions
Here are 15 examples of research questions that meet FINER criteria:
- What is the effectiveness of a 8-week peer support program in reducing compassion fatigue among emergency department nurses in tertiary care hospitals?
- How does implementation of a barcode medication administration system affect medication error rates in medical-surgical units over a 6-month period?
- What are the experiences of parents whose children receive pain management through nurse-led distraction techniques versus standard pharmacological interventions in pediatric oncology units?
- Does a 12-week music therapy intervention improve cognitive function and reduce agitation in patients with moderate to severe dementia in residential care facilities?
- What is the cost-effectiveness of nurse-led telehealth monitoring compared to traditional home visits for managing chronic heart failure in rural communities over 12 months?
- How does a nurse-driven hand hygiene education program using real-time feedback technology impact hospital-acquired infection rates in intensive care units?
- What barriers do first-time mothers from underserved communities face in accessing postpartum nursing support within the first 6 weeks after delivery?
- Is negative pressure wound therapy more effective than standard wound dressings in healing stage III pressure ulcers among immobile elderly patients in long-term care facilities?
- How does participation in a 6-week cultural competency training program affect nurses’ attitudes and behaviors when caring for immigrant patients in urban emergency departments?
- What is the relationship between nurse-patient communication quality and patient satisfaction with pain management in postoperative orthopedic surgery patients?
- How do oncology nurses experience moral distress when providing end-of-life care in hospitals with limited palliative care resources?
- Does the use of electronic health record reminder systems improve adherence to fall prevention protocols among nurses in rehabilitation units over 3 months?
- What is the effectiveness of nurse-led diabetes self-management education delivered via mobile app compared to in-person education in improving HbA1c levels over 6 months?
- How does kangaroo care performed by nurses affect physiological stability and weight gain in premature infants (28-32 weeks gestation) in neonatal intensive care units?
- What factors predict job satisfaction and retention among newly graduated nurses during their first year of practice in critical care settings?
