Primary and Secondary Data
Primary data is gathered from patients through experiments, interviews, and questionnaires specifically created for comprehending and resolving the current healthcare issue. However, collecting primary data is expensive since the organization or agency conducting the treatment must invest money and human resources (Benedictine University Library, 2022) (Primary and Secondary Data).
The provider is directly in charge of and overseeing the data collection (Surbhi, 2020). Moreover, numerous techniques help to gather data, including surveys, observations, physical examinations and mailed questionnaires. Furthermore, forms completed and sent by enumerators, in-person and telephone interviews, focus groups, and case studies.
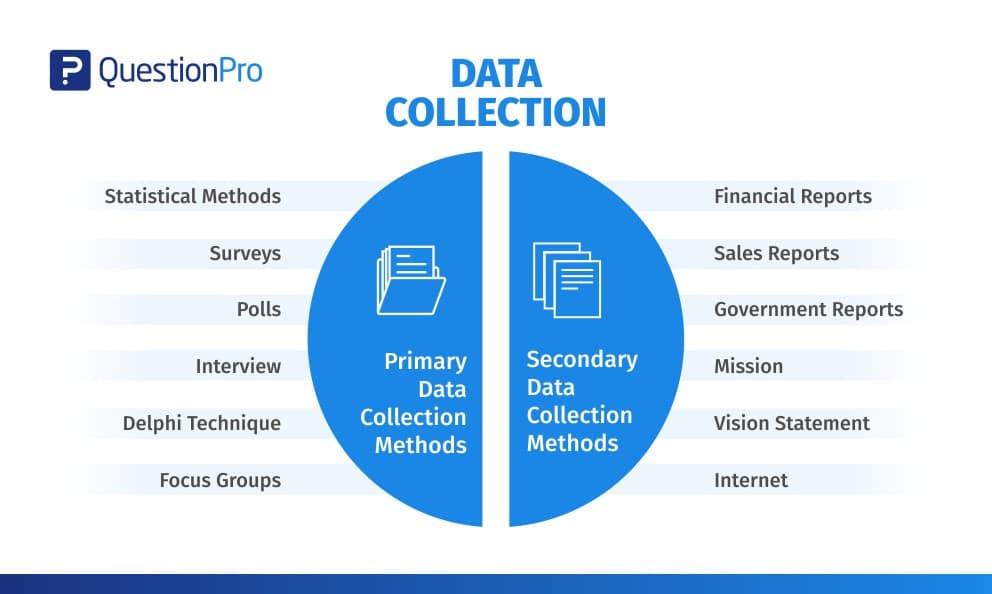
On the other hand, secondary data refers to information already gathered and recorded by someone other than the user. More so, for a reason unrelated to the current study issue. Secondary data has many benefits, including availability and saving the researcher time and money (Surbhi, 2020) (Primary and Secondary Data).
However, there are some drawbacks because the information is being gathered for reasons unrelated to the issue. Hence, means that its applicability may be constrained in several ways, including relevance and accuracy. Additionally, the goal and approach used to collect the data may not be appropriate for the current circumstances. Therefore, it is crucial to consider these shortcomings before using secondary data (Surbhi, 2020).
Large government institutions, healthcare facilities, other researchers, and publications produced by organizations as part of organizational record-keeping are examples of secondary data sources (Benedictine University Library, 2022). Conclusively, the information remain retrieved from a broader range of data files (Primary and Secondary Data).
Data for the EHR comes from numerous sources. A patient’s medical history, diagnoses, prescriptions, treatment plans, dates of immunizations, allergies, radiological pictures, and laboratory and test results are among the primary data coming from the patient or care provider’s input (University of Washington, 2023). It defines the purest form of electronic clinical data, and it remain collected at the point of care in hospitals, clinics, or other healthcare facilities.
Administrative data, claims-based datasets, electronic health records, health surveys, patient or illness or both registries, quality improvement programs, and data from ongoing trials are all secondary data sources for the EHR. Both primary and secondary data elements are helpful in patient care as they provide the needed evidence base for reference and decision-making.
References
Surbhi, S. (2020, July 13). Difference between primary and secondary data. Key Differences. https://keydifferences.com/difference-between-primary-and-secondary-data.html
Benedictine University Library. (2022, August 19). Research guides: Public health research guide: Primary & secondary data definitions. Research Guides at Benedictine University Library. https://researchguides.ben.edu/c.php?g=282050&p=4036581#
University of Washington. (2023, January 18). Library guides Data resources in the health sciences: Clinical data. Library Guides at University of Washington Libraries. https://guides.lib.uw.edu/hsl/data/findclin
