Heart Disease-Nursing Paper Examples
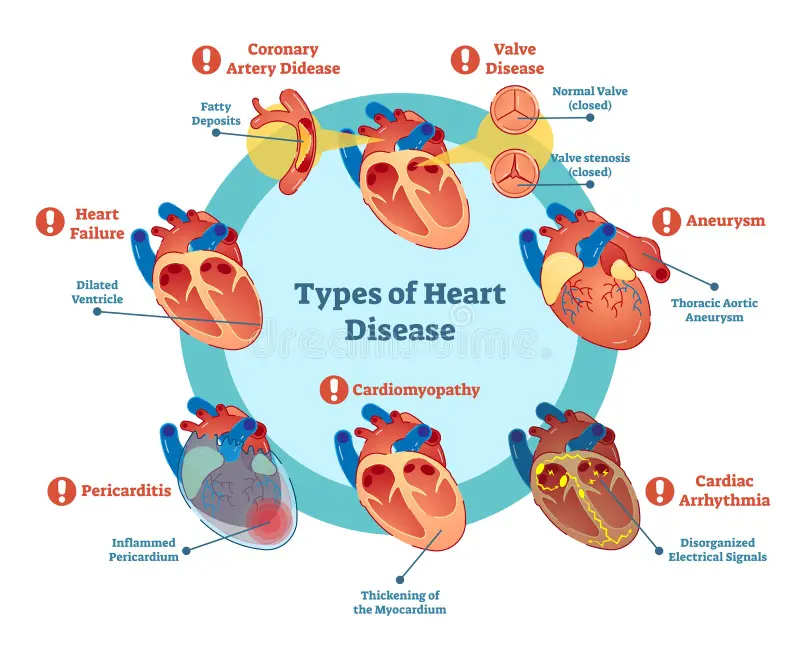
Heart disease constitutes a collection of heart conditions like stroke, coronary heart disease, peripheral arterial disease, and cardiomyopathy, which affect heart muscles and blood vessels (Peters & Schneider, 2021). Furthermore, the risk of developing these conditions can be attributed to genetic and environmental factors (Heart Disease-Nursing Paper Examples).
Heart Disease-Nursing Paper Examples
Genes are integral factors controlling every aspect of the cardiovascular system, such that any mutation in the gene increases the risk of developing heart disease (Hershberger et al., 2021). Similarly, Peters and Schneider (2021) illustrate that environmental factors like polluted air, lead, arsenic, and excess heat also increase the risk of heart disease (Heart Disease-Nursing Paper Examples).
The interactions between genes and the environment influence the development of heart disease, with the subtle genomic variations in individuals determining their response to exposure to environmental factors. For instance, Henpita et al. (2023) observe that exposure to radiation causes familial dilated cardiomyopathy, which affects the heart’s role in pumping blood due to the overdilation of heart walls and chambers.
Consequently, the low-dose X-ray beams damage DNA, resulting in mutations that enhance the development of cells into tumors and the dilation of heart walls and chambers. Moreover, the radiation can cause mutations in the TTN gene, impeding it from providing instructions for creating titin protein (Hershberger et al., 2021)(Heart Disease-Nursing Paper Examples).
The protein forms muscle structures necessary for constriction and dilation of the heart when pumping blood. Therefore, radiation-TTN interactions increase the risk of familial dilated cardiomyopathy, contributing to heart failure and death (Heart Disease-Nursing Paper Examples).
Regular exercise can help improve heart health and reduce the effects of familial dilated cardiomyopathy. It is a suitable alternative to pharmacological treatment since it can help stabilize heart function by reducing myocardial fibrosis (Moreira et al., 2020) (Heart Disease-Nursing Paper Examples).
Additionally, exercise reduces TTN gene expressions, increasing the protection of the heart against familial dilated cardiomyopathy. Subsequently, the exercise intensity should be moderate to prevent complications like chest pain and. In addition, shortness of breath, and heart palpitations associated with highly intense activity (Heart Disease-Nursing Paper Examples).
References
Henpita, C., Vyas, R., Healy, C. L., Kieu, T. L., Gurkar, A. U., Yousefzadeh, M. J., … & Niedernhofer, L. J. (2023). Loss of DNA repair mechanisms in cardiac myocytes induces dilated cardiomyopathy. Aging Cell, e13782. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13782
Hershberger, R. E., Cowan, J., Jordan, E., & Kinnamon, D. D. (2021). The complex and diverse genetic architecture of dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation Research, 128(10), 1514-1532.https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318157
Moreira, J. B., Wohlwend, M., & Wisløff, U. (2020). Exercise and cardiac health: physiological and molecular insights. Nature Metabolism, 2(9), 829-839. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-020-0262-1
Peters, A., & Schneider, A. (2021). Cardiovascular risks of climate change. Nature Reviews Cardiology, 18(1), 1-2. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-020-00473-5
