Evaluating Primary Sources (Journal Theories)
Primary sources describe original events, including diaries, journals, speeches, interviews, and maps (Yaco et al., 2020). Researchers identify primary sources based on the material it was written on, which can be scrap paper or scribbled in pencil. Besides, these sources can narrate an event using metaphors or symbols. Ideally, the authors must have been audiences of the primary source to describe an event as it occurred. In this case, researchers should consider the source’s credibility by examining the period in which it was written, its descriptive and prescriptive nature, benefits, and limitations (Journal Theories).
Evaluating Secondary Sources
Secondary sources are analyzed versions of primary sources consisting of summaries, interpretations, and reorganization of the sources (Martins et al., 2018). In addition, the sources may include literary criticisms and systematic literature reviews. Researchers evaluate these sources by determining whether the authors are scholars in the field of the study material. In addition, the source must also reference primary and other secondary sources, including in-text citations and bibliographies for the identified sources (Journal Theories).
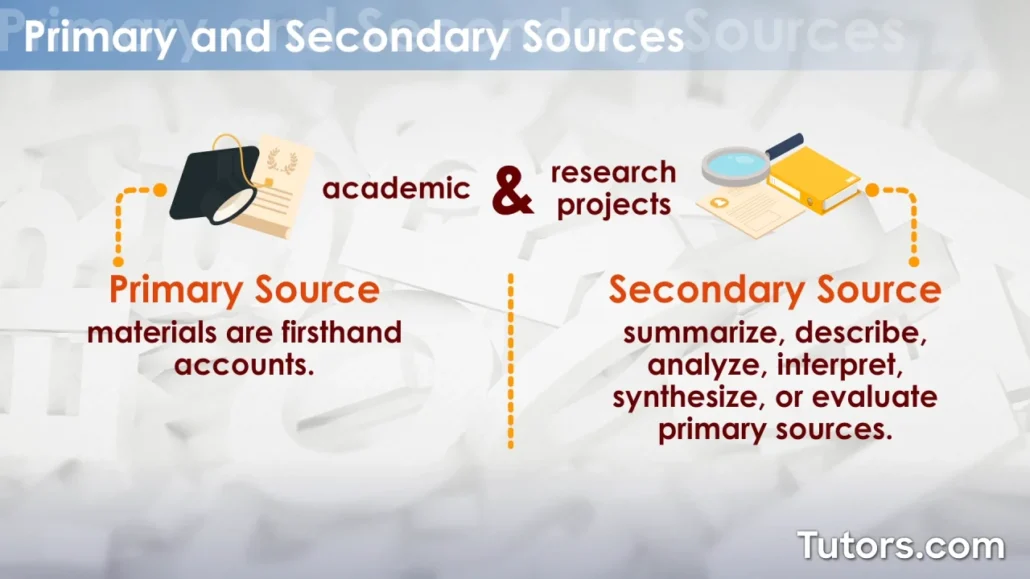
Compare and Contrast Primary and Secondary Sources
Experts write primary and secondary sources to provide information necessary during research. However, secondary sources contain bibliographies and in-text citations of other secondary and primary sources, while primary sources contain original information that does not refer to any other sources (Wiley et al., 2020). Also, primary sources comprise a historical event, which can be used as evidence, while secondary sources describe the historical event while referencing primary sources (Gwee & Gwee, 2018). Moreover, primary sources contain raw information requiring interpretation, while secondary sources interpret and describe this original information (Journal Theories).
Identify Research Methods
The research methods employed in primary research include interviews, case studies, observations, and surveys. Yaco et al. (2020) observe that primary methods improve research by providing first-hand information and conclusively answering specific research questions. However, these methods can be costly, time-consuming, and easily biased, resulting in inaccurate research results. On the other hand, secondary research methods include summaries of public records, government publications, review articles, and meta-analyses (Gwee & Gwee, 2018). These methods are essential in formulating appropriate research designs but may also provide inaccurate or irrelevant information that can lead to biased research results (Journal Theories).
Other Criteria
Tertiary sources constitute the compilation, organization, and indexing of primary and secondary sources during the research (Alomi et al., 2021). The sources include dictionaries, directories, and handbooks. Tertiary sources provide background information for research but lack originality or analysis of the information sources (Journal Theories).
References
Alomi, Y. A., Aljohani, H. S. S., Albatil, A. A. B., Al Shams, A. A., & Alshams, S. A. M. (2021). Dental drug information tertiary resources: a new initiative project in Saudi Arabia. PTB Reports, 7(2). http://dx.doi.org/10.5530/PTB.2021.7.9
Gwee, J., & Gwee, J. (2018). The Research Rhombus. The Case Writer’s Toolkit, 63-86. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7173-7_4
Martins, F. S., da Cunha, J. A. C., & Serra, F. A. R. (2018). Secondary data in research–uses and opportunities. PODIUM sport, leisure, and tourism review, 7(3). https://doi.org/10.5585/podium.v7i3.316
Wiley, J., Griffin, T. D., Steffens, B., & Britt, M. A. (2020). Epistemic beliefs about the value of integrating information across multiple documents in history. Learning and Instruction, 65, 101266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2019.101266
Yaco, S., Ramaprasad, A., & Syn, T. (2020). Themes in recent research on integrating primary source collections and instruction. portal: Libraries and the Academy, 20(3), 449-474. https://doi.org/10.1353/pla.2020.0025
