Discover everything you need to know about Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) programs, from curriculum and admission requirements to costs and employment outlook. Learn why accreditation matters and make an informed choice for your nursing education.
What is an ADN?

An Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) is a two-year program designed to provide students with the essential knowledge and skills needed to become registered nurses (RNs). ADN programs offer a balanced blend of classroom instruction and practical clinical experience, preparing students for entry-level roles in healthcare settings. This educational path is widely favored for those looking to kickstart a career in nursing.
How Long Does an ADN Take?
Typically, an ADN program spans two years for completion. However, the precise timeline may be influenced by factors like class scheduling, clinical hours, and any potential prerequisites. The curriculum encompasses a broad spectrum of subjects, covering anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and core nursing principles, ensuring a comprehensive education in the fundamentals of nursing.

Curriculum for ADN
The ADN program’s curriculum strikes a balance between theoretical knowledge and hands-on clinical training. Students engage with courses such as anatomy and physiology, pharmacology, medical-surgical nursing, pediatrics, obstetrics, and mental health nursing. Moreover, practical experiences in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities allow students to apply their learning in real-world settings.
Admission Requirements for ADN
Institutions may impose varying admission criteria for ADN programs. However, common prerequisites include a high school diploma or its equivalent, a satisfactory GPA, and completion of an application form. Additionally, some programs may necessitate proof of prerequisite courses, such as biology, chemistry, and mathematics, to ensure students possess a foundational understanding of relevant subjects.
What are the Prerequisites for ADN?
Prerequisites for ADN programs often encompass fundamental science courses like biology, chemistry, and anatomy. These foundational subjects provide a crucial understanding of the human body and medical terminology, forming the bedrock for success in nursing education. Additionally, some programs may incorporate introductory psychology or sociology courses to foster the development of essential interpersonal skills needed in healthcare settings.
How Much Does an ADN Degree Cost?
The cost of pursuing an ADN program can fluctuate significantly based on factors like location, institution, and whether the student opts for a public or private college. On average, tuition and associated fees for an ADN program can range from $5,000 to $40,000. It is imperative for prospective students to proactively explore financial aid options, scholarships, and grants to mitigate these expenses.
Is an ADN Program Worth It?

An ADN program stands as a cost-effective and expedient route towards achieving the status of a registered nurse. Graduates often find themselves in fulfilling and well-compensated roles within various healthcare settings. Moreover, an ADN can serve as a stepping stone for those harboring ambitions of pursuing advanced degrees in nursing, solidifying its value as a strategic investment in one’s professional journey.
Why Is ADN Program Accreditation Important?
Accreditation serves as a vital assurance that an ADN program upholds specific educational standards, ensuring the delivery of quality education. Graduating from an accredited program enhances the likelihood of passing the licensing examination and securing employment. Additionally, accreditation may serve as a prerequisite for pursuing advanced degrees or seamlessly transferring credits to other educational institutions.
What is the Employment Outlook for ADN?
Projections indicate a significant surge in demand for registered nurses in the coming years. Graduates of ADN programs are poised to find abundant opportunities in various healthcare settings including hospitals, clinics, long-term care facilities, and more. Armed with a diverse skill set and practical experience, ADN-educated nurses are well-positioned for a range of specialized roles within the field.
What Makes This Major Unique?
The distinctive strength of an ADN program lies in its targeted curriculum, which expeditiously readies students for the practical demands of nursing. By emphasizing hands-on clinical experience alongside classroom learning, ADN graduates enter the workforce armed with a robust foundation in patient care, critical thinking, and effective communication skills.
Is it best to take the ADN route for nursing (then take the RN-to-BSN) or BSN?
The choice between the ADN and BSN path hinges on individual goals and circumstances. ADN programs offer a more direct route to becoming an RN, enabling graduates to enter the workforce sooner. Conversely, pursuing a BSN provides a broader education with additional coursework in leadership, research, and community health. This can potentially open doors to specialized roles and higher-level positions in nursing.
ADN Career Salary:
Upon completion of an ADN program and obtaining licensure, registered nurses (RNs) can expect a competitive salary. The average annual earnings for ADN-educated nurses range from $60,000 to $80,000, with factors like location, specialization, and experience influencing income. Moreover, nurses with ADNs often find lucrative opportunities for overtime and shift differentials, further enhancing their earning potential.
Nursing Careers with an Associate Degree:
An Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) opens doors to a variety of rewarding nursing careers. ADN-educated nurses can excel in roles such as staff nurse, charge nurse, or clinical nurse coordinator in settings like hospitals, long-term care facilities, and clinics. Additionally, they may specialize in areas like medical-surgical, pediatric, or geriatric nursing, aligning with their interests and strengths.
Can I get my Associate Degree in Nursing online?
Yes, many accredited institutions offer online ADN programs. These programs provide flexibility for students who may have work or family commitments. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the program includes in-person clinical experiences, as hands-on training is integral to nursing education. Prospective students should also verify that the online program meets the necessary accreditation standards.
Differences between an ADN and a BSN:
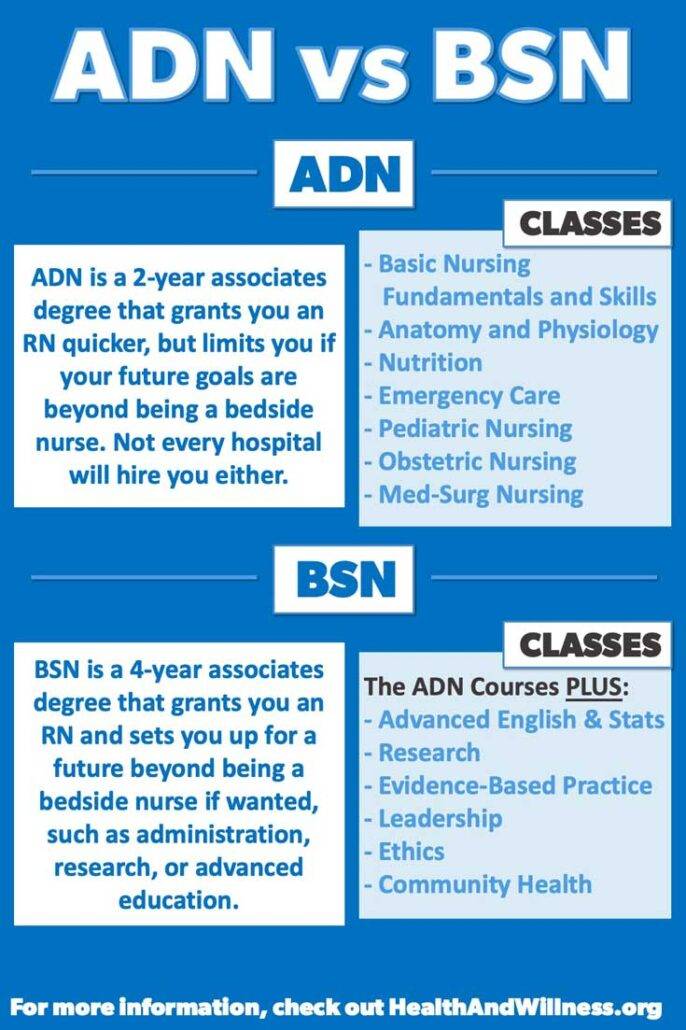
- Educational Duration: ADN typically spans 2 years, while BSN entails 4 years of study.
- Curriculum Emphasis: ADN focuses on core nursing competencies; BSN includes advanced coursework in leadership, research, and community health.
- Career Options: BSN may offer broader career opportunities and potential for higher-level roles.
- Clinical Experience: Both programs incorporate hands-on training, with ADN providing substantial clinical exposure.
- Prerequisites: ADN may have fewer prerequisite courses compared to BSN, expediting the path to registered nurse status.
Questions to Ask When Choosing an ADN Program:
- Accreditation: Is the program accredited by a recognized nursing accreditation body?
- Clinical Experience: What opportunities are provided for hands-on clinical training?
- Faculty Credentials: Are the instructors experienced and qualified in nursing education?
- Licensing Pass Rates: What is the program’s success rate for graduates passing the NCLEX exam?
- Cost and Financial Aid: What are the tuition fees, and are there financial aid options available?
- Student Support Services: Are there resources for academic assistance and career guidance?
- Graduate Outcomes: What types of positions do graduates typically secure after completing the program?
NCLEX and Licensing:
After completing an ADN program, graduates must pass the NCLEX-RN exam to obtain licensure as a registered nurse. The NCLEX assesses a nurse’s ability to apply safe and effective care principles. Adequate preparation through review courses and practice exams is crucial. Once licensed, nurses must meet continuing education requirements to maintain their credentials and stay updated with evolving healthcare practices.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the journey through an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) program offers a succinct yet comprehensive path towards becoming a registered nurse. Balancing theoretical knowledge with hands-on clinical practice, this two-year program equips graduates with the essential skills and expertise needed in the dynamic healthcare sector. With a strong employment outlook and opportunities for advancement, the ADN route stands as a valuable investment in one’s nursing career. Ultimately, the choice between ADN and BSN should be made based on individual goals, with both pathways offering unique advantages for aspiring nurses. It’s a decision that can shape a fulfilling and impactful career in healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What does ADN mean in nursing?
- ADN stands for Associate Degree in Nursing. It is a two-year undergraduate program designed to equip students with the fundamental knowledge and skills needed to become registered nurses (RNs).
- What is the difference between ADN and ASN?
- ADN (Associate Degree in Nursing) and ASN (Associate of Science in Nursing) are terms often used interchangeably. Both refer to the same type of nursing program, a two-year associate degree program that prepares students to become registered nurses. The key difference is in the naming convention, with some institutions using “ADN” while others use “ASN” to denote this type of nursing program.
- Can ADN do the same as BSN?
- ADN-prepared nurses and BSN-prepared nurses can perform many of the same tasks and roles in clinical settings. Both can provide direct patient care, administer medications, and collaborate with healthcare teams. However, BSN-educated nurses may have additional training in areas like leadership, research, and community health, which can lead to broader career opportunities and potential for higher-level roles.
- Is ADN better than ASN?
- ADN and ASN refer to the same type of nursing program, so there is no inherent difference in the education provided. The choice between ADN/ASN and other nursing programs (like BSN) depends on individual goals and circumstances. Some may find the two-year ADN/ASN program a more accessible and efficient way to become a registered nurse, while others may prefer the broader education and potential career opportunities offered by a four-year BSN program. It’s important to consider one’s long-term career aspirations when making this decision.


