Nursing informatics is a rapidly growing field that integrates nursing science, computer science, and information technology to enhance patient care and streamline healthcare systems. As healthcare continues to embrace digital transformation, understanding nursing informatics and its applications is crucial for improving efficiency, communication, and patient outcomes.
We explore the ANA definition of nursing informatics, its evolution, effective communication with informatics nurses, hospital utilization, application of nursing theory, the SDLC framework, and real-world topics shaping the field.
ANA Definition of Nursing Informatics
According to the American Nurses Association (ANA), nursing informatics is:
“A specialty that integrates nursing science, computer science, and information science to manage and communicate data, information, knowledge, and wisdom in nursing practice.”
This definition emphasizes the role of nursing informatics in enhancing decision-making, improving clinical workflows, and optimizing healthcare delivery through technology. Informatics nurses play a critical role in developing, implementing, and optimizing electronic health records (EHRs), clinical decision support systems, and other healthcare IT solutions.
The key goals of nursing informatics include:
- Improving patient care through evidence-based decision-making.
- Enhancing workflow efficiency for nurses and healthcare providers.
- Ensuring seamless health information exchange (HIE) across facilities.
- Strengthening data security and compliance with healthcare regulations.
Nursing informatics bridges the gap between technology and patient-centered care, ensuring that digital innovations align with nursing practice.
Evolution of Nursing Informatics
Nursing informatics has evolved alongside advancements in healthcare technology and data management. Below is a brief timeline highlighting key milestones:
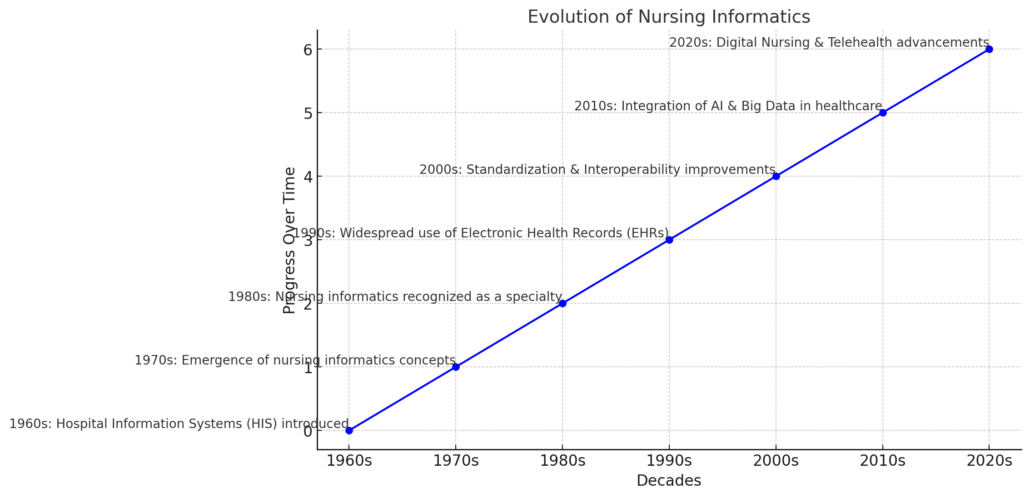
1. 1960s – The Birth of Healthcare Computing
- Early computers were introduced in hospitals to automate administrative tasks.
- The first Hospital Information Systems (HIS) were developed to digitize patient records.
2. 1970s – Emergence of Nursing Informatics Concepts
- The first Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) were created, although they were basic.
- Nurses started using computers for documentation and research.
3. 1980s – Formal Recognition of Nursing Informatics
- Nursing informatics emerged as a recognized specialty.
- The American Nurses Association (ANA) established the first Nursing Informatics Guidelines.
- Nursing informatics courses were introduced in universities.
4. 1990s – Rapid Technological Growth
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs) became more widespread.
- The Internet transformed communication and data sharing in healthcare.
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was passed, emphasizing patient data security.
5. 2000s – Standardization and Interoperability
- The Meaningful Use Initiative encouraged EHR adoption.
- Barcoding and RFID technology improved medication safety.
- Cloud-based health IT systems enabled remote patient monitoring.
6. 2010s – Integration of AI and Big Data
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and predictive analytics began influencing patient care.
- The growth of telehealth and mobile health apps transformed nursing workflows.
7. 2020s – The Era of Digital Nursing
- AI-powered decision-support systems assist nurses in patient care.
- Advanced robotics and automation improve efficiency in hospitals.
- The demand for informatics nurses continues to rise as healthcare technology advances.
The evolution of nursing informatics reflects a shift from simple record-keeping to complex data-driven decision-making, making informatics nurses key players in modern healthcare.
How to Effectively Communicate with Informatics Nurses
Effective communication with informatics nurses is essential for successful technology adoption and problem-solving in healthcare. Here’s how to foster better collaboration:
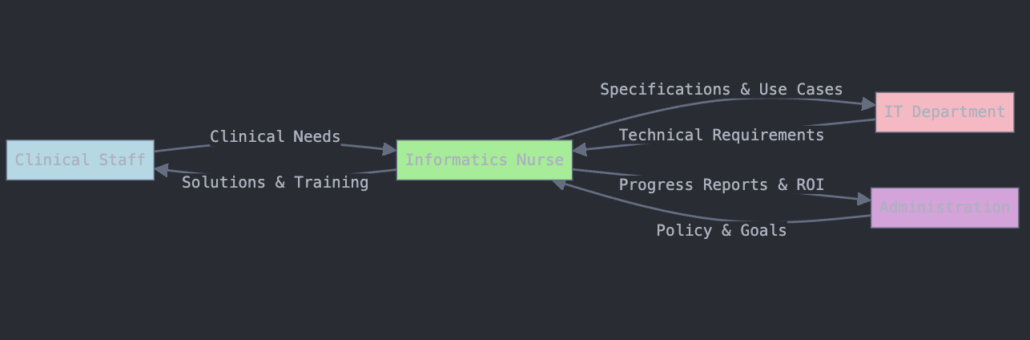
- Use Structured Communication Methods
- Implement SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) to ensure clarity in discussions.
- Encourage Active Participation
- Include informatics nurses in clinical meetings and decision-making processes related to health IT.
- Provide Clear Feedback
- Offer specific examples of challenges or workflow inefficiencies to help informatics nurses develop better solutions.
- Leverage Visual Aids
- Use screenshots, diagrams, and real-time demonstrations when discussing system issues.
- Stay Open to Change and Training
- Informatics nurses often introduce new digital tools—actively participate in training and provide constructive feedback.
By improving communication, healthcare teams can enhance collaboration and optimize the impact of nursing informatics.
How Do Hospitals Utilize Informatics Nurses?
Hospitals rely on informatics nurses for various clinical, administrative, and technical functions, including:
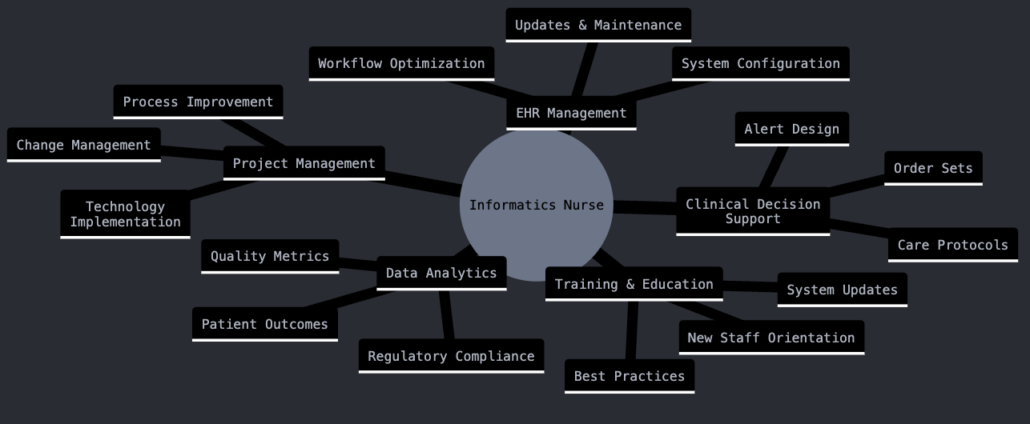
- EHR Implementation & Optimization – Customizing electronic health records to improve usability.
- Workflow Efficiency – Identifying inefficiencies and developing technology-driven solutions.
- Interdisciplinary Training – Educating staff on new digital tools and best practices.
- Data Analytics & Decision Support – Using predictive analytics to enhance patient care.
- Health IT Security – Ensuring compliance with HIPAA and cybersecurity regulations.
By integrating informatics nurses, hospitals can enhance patient safety, efficiency, and healthcare outcomes.
How to Use Nursing Theory in Nursing Informatics
Nursing theories guide the development of technology solutions that align with patient-centered care. Informatics nurses apply nursing theory in the following ways:
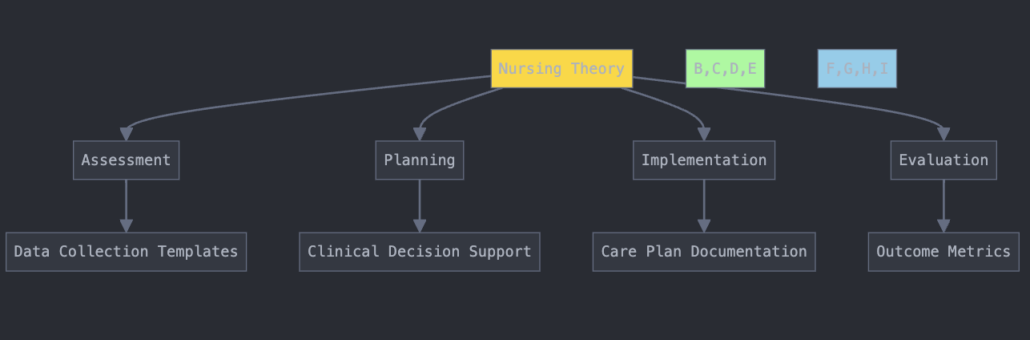
- Benner’s Novice-to-Expert Model – Designing EHR interfaces and decision-support tools suited to different experience levels.
- Watson’s Theory of Human Caring – Ensuring EHR documentation reflects holistic, compassionate care.
- Systems Theory – Developing interoperable systems that connect different hospital departments seamlessly.
- Iowa Model of Evidence-Based Practice – Embedding research-based guidelines into clinical decision support tools.
By integrating nursing theory with informatics, healthcare organizations can enhance both clinical and technological practices.
Nursing Informatics SDLC (Systems Development Life Cycle)
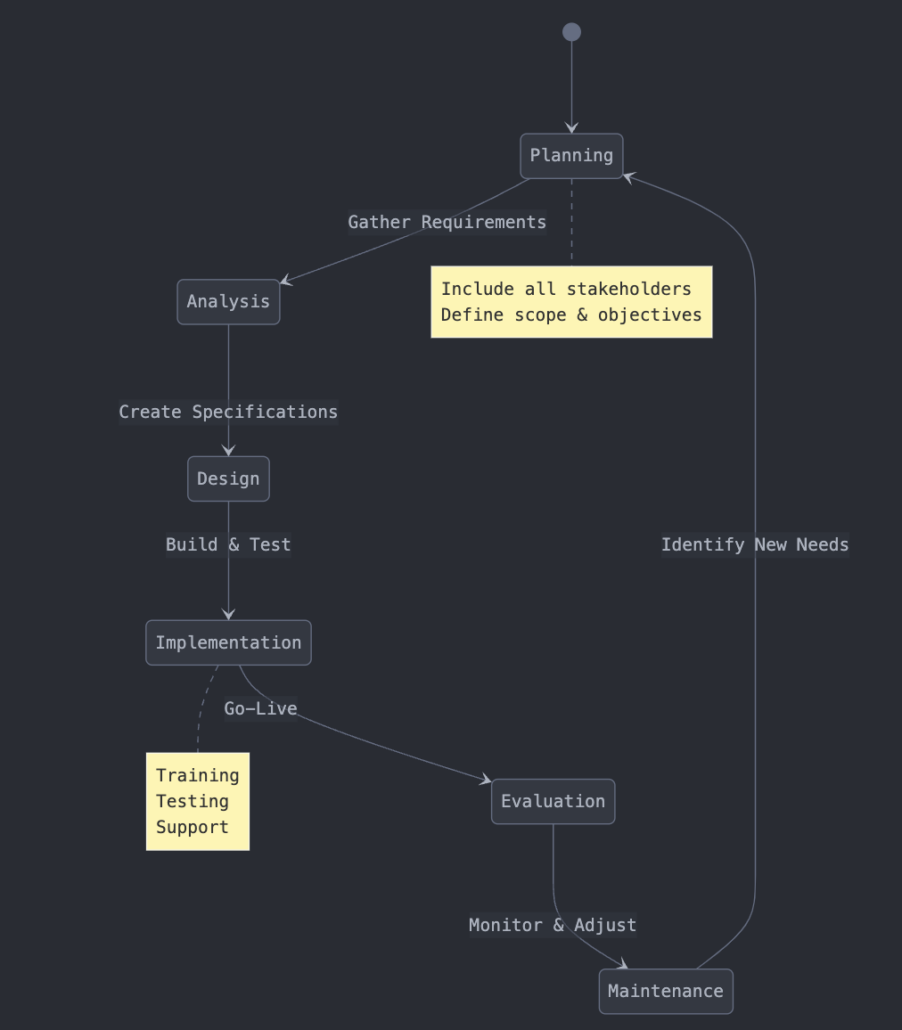
Phases of the Nursing Informatics SDLC
The six phases of the SDLC and the role of nursing informatics in each are detailed below:
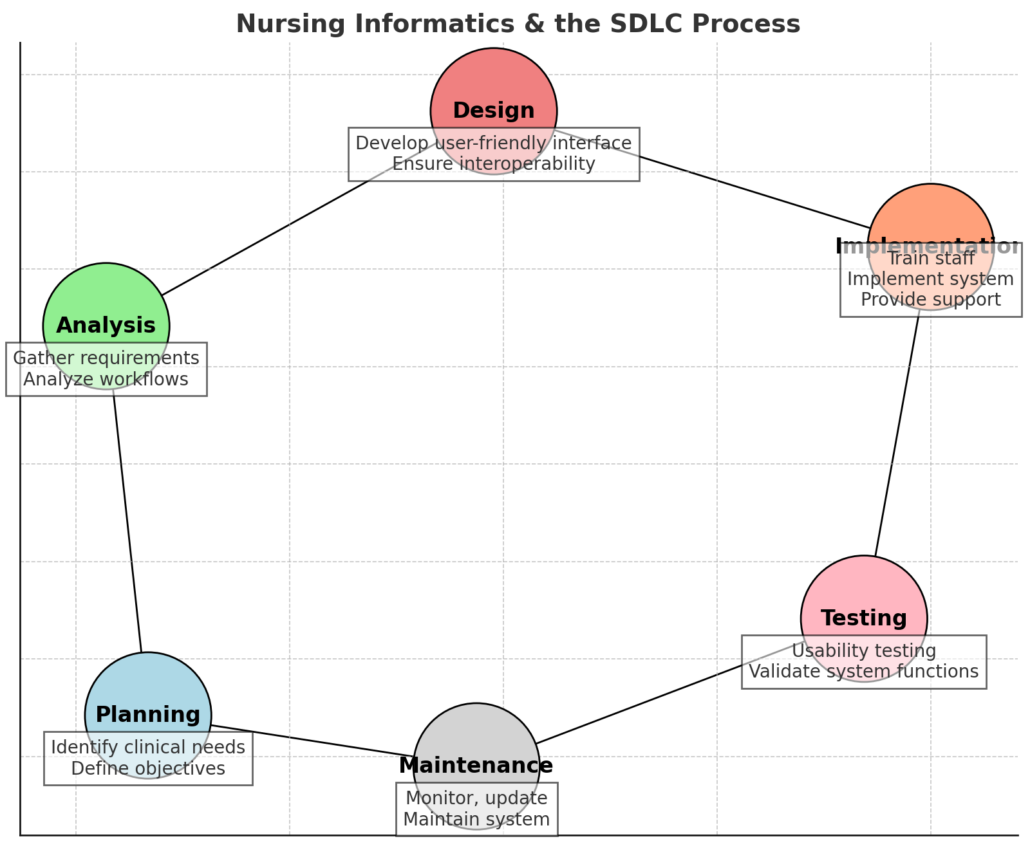
1. Planning Phase 🏗️
Goal: Identify problems, define objectives, and establish system requirements.
- Informatics nurses help identify clinical needs and workflow inefficiencies.
- Assess feasibility, budget constraints, and regulatory requirements (e.g., HIPAA).
- Engage nurses, physicians, and IT specialists in discussions on system expectations.
2. Analysis Phase 🔍
Goal: Gather detailed requirements and assess existing healthcare workflows.
- Conduct workflow analysis to identify gaps and inefficiencies.
- Gather user input through surveys, interviews, and observation.
- Ensure compliance with healthcare regulations and data security policies.
3. Design Phase 🎨
Goal: Develop a user-friendly and efficient system architecture.
- Informatics nurses provide feedback on interface usability and workflow integration.
- Design system features such as clinical decision support tools (CDS), data entry forms, and reporting dashboards.
- Focus on interoperability to ensure seamless data exchange across healthcare systems.
4. Implementation Phase 🚀
Goal: Install the system, train staff, and transition into full operation.
- Train nurses, physicians, and healthcare staff on system usage.
- Implement role-based access controls to enhance security.
- Conduct pilot testing in select departments before full-scale rollout.
- Provide ongoing support to ensure a smooth transition.
5. Testing Phase 🛠️
Goal: Identify errors, test system performance, and validate functionalities.
- Conduct usability testing with real users (nurses, clinicians).
- Test system response time, data integrity, and security compliance.
- Gather feedback from clinical staff and make necessary adjustments.
6. Maintenance Phase 🔄
Goal: Ensure long-term usability, update systems, and provide support.
- Monitor system performance and address issues promptly.
- Provide ongoing training and user support.
- Implement software updates and ensure compliance with evolving healthcare regulations.
By following these SDLC phases, healthcare organizations can develop and maintain reliable, efficient, and user-friendly nursing informatics systems that improve patient outcomes and streamline nursing workflows.
Nursing Informatics and Real-World Topics
Nursing informatics is at the forefront of healthcare transformation, shaping how technology enhances patient care, streamlines clinical workflows, and improves decision-making. As healthcare technology advances, informatics nurses play a critical role in ensuring its effective and ethical implementation.
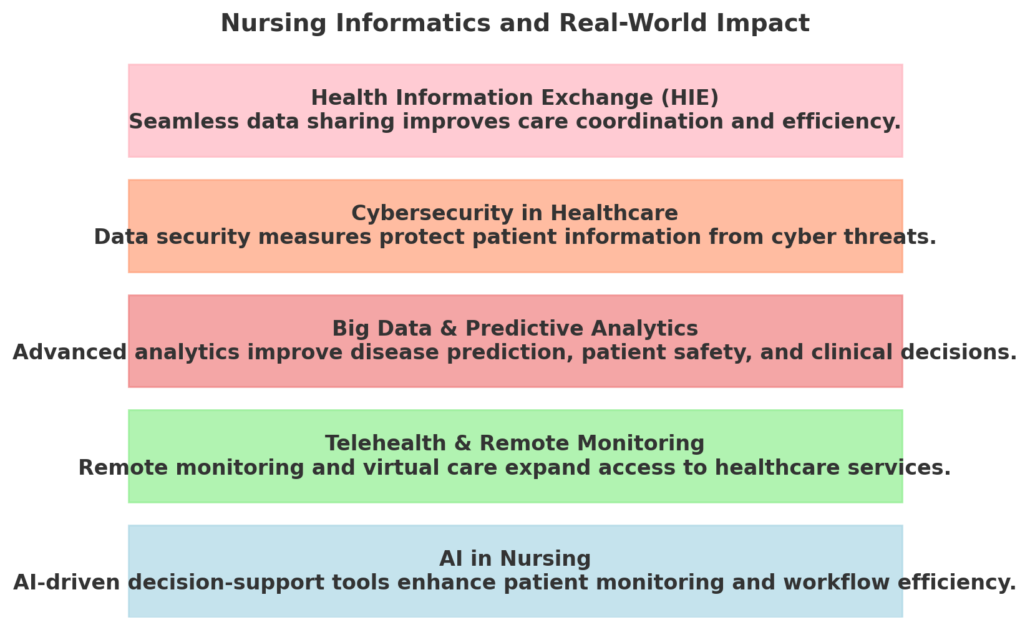
Here are key real-world topics where nursing informatics is making a significant impact:
1. AI in Nursing 🤖
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered clinical decision support systems (CDSS) assist nurses by analyzing vast datasets and predicting patient deterioration.
- AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants streamline nursing workflows by handling routine patient inquiries.
2. Telehealth & Remote Monitoring 📡
- Informatics nurses facilitate telemedicine solutions, enabling patients to receive virtual care from anywhere.
- Remote patient monitoring (RPM) technologies allow continuous tracking of vital signs, reducing hospital readmissions and improving chronic disease management.
3. Big Data & Predictive Analytics 📊
- Advanced data analytics tools help predict disease outbreaks, patient deterioration, and medication side effects.
- Informatics nurses analyze trends in electronic health records (EHRs) to improve clinical decision-making and reduce errors.
4. Cybersecurity in Healthcare 🔒
- With the rise in cyberattacks on healthcare systems, informatics nurses play a key role in ensuring data protection and compliance with HIPAA regulations.
- Implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA), encryption, and access control safeguards patient information.
5. Health Information Exchange (HIE) 🔄
- Informatics nurses support seamless data exchange between hospitals, clinics, and healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care.
- Standardized interoperability frameworks allow faster diagnosis and better coordination between healthcare teams.
Read More on;
- Nursing Informatics Proposal Project Example – Best in 2025
- Nursing Informatics Project Proposal NURS 6051 Example
- Nursing Informatics Theory The DIKW Framework – A Simplified Guide for Nurses
- How to Write a Nursing Informatics Essay in 2025
- 120 Nursing Informatics Topics and Nursing Research Paper Examples
